Introduction
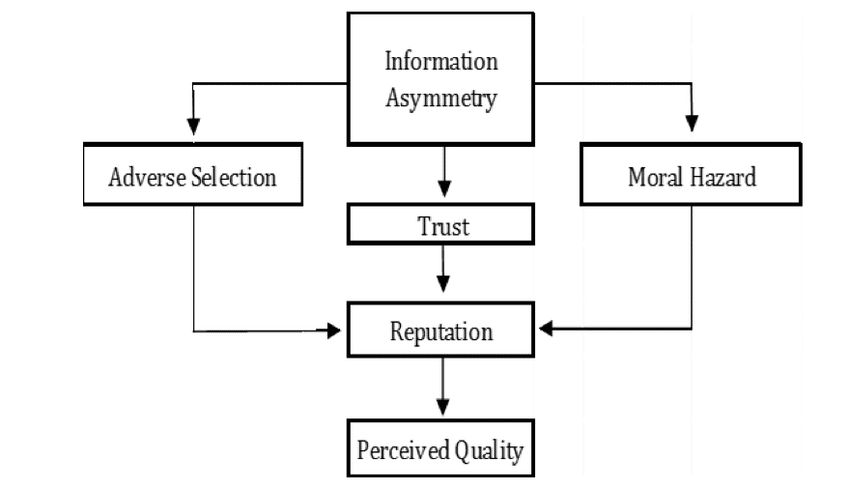
In the realm of decision-making, an insidious challenge arises when buyers and sellers interact in markets characterized by information asymmetry. The Lemon Market Problem, a mental model deeply rooted in human psychology, plays a significant role in shaping our day-to-day choices. This concept refers to the adverse selection problem, where the quality of goods or services is uncertain due to information asymmetry, leading to irrational decisions that contradict the buyers’ best interests. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the relevance of the Lemon Market Problem in decision-making processes, examine its prevalence in various contexts, analyze the psychological biases contributing to this phenomenon, and provide practical strategies to help readers overcome this cognitive trap.
The Relevance of the Lemon Market Problem in Decision-Making: The Lemon Market Problem is highly relevant in decision-making processes, especially in situations where buyers must rely on sellers for information about the quality of goods or services. This model sheds light on the challenges that arise when one party possesses superior knowledge or information compared to the other. Understanding this mental model is essential for making informed decisions and avoiding potential pitfalls associated with information asymmetry.
Examples of the Lemon Market Problem in Various Contexts
- Used Car Market: The Lemon Market Problem is prominently observed in the used car market. Buyers lack complete information about the condition and history of the vehicles they are considering purchasing, while sellers possess superior knowledge. As a result, buyers may unwittingly purchase low-quality “lemon” cars at inflated prices, as sellers have the advantage of selectively disclosing information that favors their interests.
- Health and Wellness Industry: In the realm of health and wellness, the Lemon Market Problem manifests when consumers encounter a flood of products, treatments, and supplements promising miraculous results. Without access to complete and reliable information, buyers can fall prey to deceptive marketing tactics, making irrational decisions and spending their resources on ineffective or potentially harmful products.
- Online Marketplaces: E-commerce platforms, such as online marketplaces, are not exempt from the Lemon Market Problem. Sellers can misrepresent the quality or condition of their products, leading buyers to make ill-informed decisions. Reviews and ratings can help mitigate the issue to some extent, but manipulation and biased feedback can still create challenges for buyers seeking accurate information.
Mental Biases Contributing to the Lemon Market Problem:
Several cognitive biases exacerbate the Lemon Market Problem, influencing decision-making processes in situations characterized by information asymmetry. Some prominent biases include
- Confirmation Bias: Buyers may exhibit confirmation bias by seeking information that confirms their preconceived notions or desires, rather than objectively evaluating the available information. This bias can lead to the acceptance of incomplete or biased information provided by sellers.
- Illusion of Transparency: Buyers may overestimate their ability to accurately assess the quality of goods or services, assuming that their own preferences and expectations align with the seller’s claims. This illusion of transparency can lead to misplaced trust and a failure to critically evaluate available information.
- Herd Mentality: In contexts where buyers rely on the decisions of others, such as product reviews or recommendations, the herd mentality bias can lead to a lack of individual critical thinking. Buyers may follow the crowd without thoroughly evaluating the available information, potentially overlooking the Lemon Market Problem.
Strategies to Identify and Mitigate the Lemon Market Problem:
To navigate the Lemon Market Problem effectively, buyers can employ the following strategies
- Conduct Thorough Research: Buyers should invest time in gathering information from various reliable sources. Seeking expert opinions, conducting independent research, and verifying claims made by sellers can help mitigate the impact of information asymmetry.
- Seek Third-Party Verification: Relying on objective and independent third-party verification can provide buyers with more reliable information. This could include certifications, expert opinions, or unbiased reviews from trusted sources.
- Ask the Right Questions: Buyers should actively engage with sellers and ask specific questions to elicit more detailed information about the product or service being offered. This approach helps to uncover potential red flags and assess the seller’s transparency and credibility.
- Utilize Escrow Services and Guarantees: When transacting in markets where quality is uncertain, leveraging escrow services or guarantees can provide buyers with a safety net. These mechanisms ensure that payment is contingent upon the product or service meeting certain standards or expectations.
Conclusion
The Lemon Market Problem serves as a powerful mental model that influences decision-making processes when information asymmetry exists. By understanding its dynamics and the associated psychological biases, individuals can become more aware of the risks and actively mitigate the adverse effects. Thorough research, third-party verification, asking the right questions, and utilizing protective mechanisms can help individuals navigate situations characterized by information asymmetry. By actively avoiding the Lemon Market Problem, individuals can make more informed decisions, protect their best interests, and foster a marketplace characterized by transparency and trust.