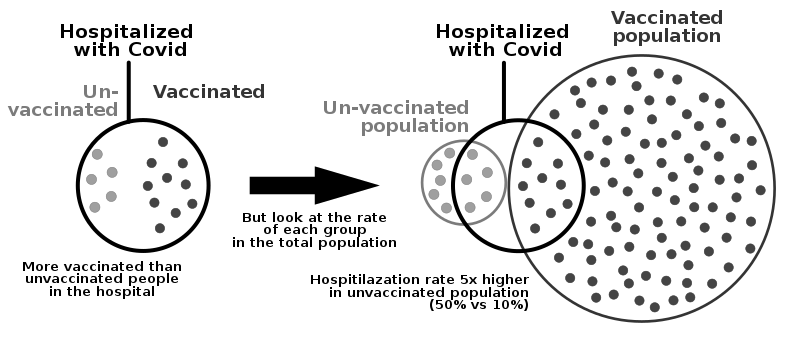
Introduction
In the realm of decision-making, our cognitive biases can often lead us astray, hindering our ability to make rational choices. One such mental model that sheds light on this phenomenon is the Neglect of Base Rate. This model refers to our tendency to disregard the statistical base rate information when making judgments or predictions, and instead, focus on specific, individual case information. The Neglect of Base Rate is deeply rooted in human psychology and can have profound implications in various decision-making contexts. In this blog post, we will explore the relevance of the Neglect of Base Rate in decision-making processes, its prevalence in our daily lives, and the consequences of succumbing to this fallacy.
The Neglect of Base Rate in Decision-Making
The Neglect of Base Rate is highly relevant in decision-making processes as it can distort our judgment and lead to irrational choices. Base rate information refers to the general probability or prevalence of an event within a specific population, while individual case information pertains to specific characteristics or details of a particular case. While both types of information are crucial for accurate decision-making, the Neglect of Base Rate occurs when individuals focus excessively on individual case information, neglecting the broader statistical context.
Anchoring in Human Psychology and Prevalence in Daily Life
The Neglect of Base Rate is anchored in several cognitive biases and heuristics that influence our thinking
- Availability heuristic: This bias refers to our tendency to rely on easily accessible or vivid examples when making judgments. When confronted with individual case information that is vivid or emotionally salient, we may overweight its significance, neglecting the underlying base rate information. For example, if we hear a highly publicized story about a person winning the lottery, we might overestimate our own chances of winning, neglecting the low base rate of such an event.
- Representativeness heuristic: This bias leads us to make judgments or predictions based on how well an individual or event matches a prototype or stereotype. When the individual case information is highly representative of a particular category or group, we tend to neglect the base rate information. For instance, if we meet a person who fits our stereotypical image of a successful entrepreneur, we may overlook the fact that most entrepreneurs actually face significant challenges and have a low success rate.
- Confirmation bias: This bias occurs when we actively seek out information that confirms our existing beliefs or expectations. By selectively focusing on information that aligns with our preconceived notions, we neglect the base rate information that may challenge or contradict our views. This confirmation bias reinforces the Neglect of Base Rate and can lead to faulty decision-making.
Examples of the Neglect of Base Rate in Context
- Personal Life Decisions: Imagine a person considering whether to invest in a particular stock. Instead of examining the historical performance and base rate of success for similar stocks in the market, they focus solely on success stories of individuals who have made significant gains. Neglecting the base rate information of the stock market’s overall volatility and the average returns, they may make an irrational decision based on anecdotal evidence, disregarding the statistical probabilities.
- Business Scenarios: In business, neglecting the base rate can lead to misguided strategies and flawed decision-making. For instance, if a company decides to launch a new product solely based on a few highly successful case studies in the industry, without considering the overall failure rate or market demand, they may neglect crucial base rate information. This oversight can result in costly investments and missed opportunities.
- Public Policy-Making: In the realm of public policy, neglecting base rate information can have significant consequences. For example, if policymakers base their decisions solely on isolated case studies of successful social programs, without considering the overall base rate of success, they may implement ineffective policies. Neglecting the broader statistical context can hinder the development of evidence-based policies that address the needs of the population as a whole.
Mental Biases Contributing to the Neglect of Base Rate
In addition to the biases mentioned earlier, several other cognitive biases contribute to the prevalence of the Neglect of Base Rate
- Overconfidence bias: Individuals tend to overestimate their own knowledge and abilities. When coupled with the Neglect of Base Rate, this bias leads individuals to rely heavily on their subjective judgment and overlook the importance of statistical information.
- Framing bias: The way information is presented can influence our decision-making. If the individual case information is framed in a compelling or emotionally charged manner, it can overshadow the base rate information, leading to biased judgments.
- Sunk cost fallacy: When individuals have invested significant resources, such as time or money, into a particular course of action, they may neglect the base rate information and continue pursuing their chosen path, even when it no longer aligns with rational decision-making.
Identifying and Avoiding the Neglect of Base Rate
To mitigate the Neglect of Base Rate and make more objective decisions, individuals can employ the following strategies
- Seek out base rate information: Actively gather and analyze relevant base rate statistics, historical data, or expert opinions to understand the broader statistical context of the decision at hand. Recognize that individual case information should be considered alongside base rate information, rather than in isolation.
- Challenge your assumptions: Actively question your initial judgments and preconceived notions. Recognize that cognitive biases can distort your perception of information, leading to the neglect of base rate. Encourage critical thinking and consider alternative perspectives.
- Conduct thorough research: Take the time to gather comprehensive information from multiple sources. Engage in rigorous analysis and evaluate the quality of evidence supporting your decision. By conducting thorough research, you can counteract the tendency to rely solely on individual case information.
- Consult experts or seek diverse opinions: Engage with individuals who possess expertise or diverse viewpoints related to the decision at hand. By soliciting input from others, you can gain insights that you may have overlooked and obtain a more balanced perspective that includes base rate information.
Conclusion
The Neglect of Base Rate is a common cognitive bias that can significantly impact decision-making processes. By overlooking base rate information and focusing excessively on individual case information, individuals risk making irrational choices that are contrary to their best interests. By recognizing the psychological underpinnings, biases, and prevalence of the Neglect of Base Rate, individuals can cultivate awareness and actively avoid this mental trap. Through the careful consideration of base rate information, the challenging of assumptions, and thorough research, individuals can enhance their decision-making abilities and make more informed and rational choices. Being mindful of the Neglect of Base Rate empowers us to navigate decision-making scenarios with greater objectivity, leading to better outcomes in our personal, professional, and public lives.