Introduction
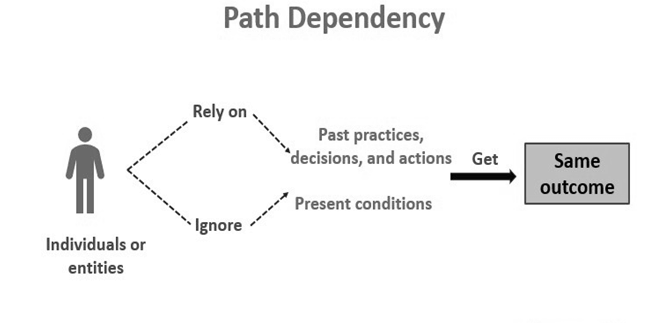
In the realm of decision-making, our choices are often shaped by the past. Path dependence, a mental model rooted in history, highlights how previous decisions or events can profoundly impact present and future choices. Defined as the idea that the options available to us are influenced by the decisions and circumstances that have come before, path dependence reveals the importance of understanding the historical context in decision-making. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of path dependence, its relevance in decision-making processes, its psychological underpinnings, and practical strategies to avoid falling into its trap.
The Relevance of Path Dependence
Path dependence recognizes that decisions made in the past can constrain or shape future possibilities. The choices we make today are not made in isolation but are influenced by a complex web of historical events, systems, and cultural factors. Understanding path dependence is crucial because it highlights the long-term consequences of decisions and encourages us to consider the broader context in which we operate.
Anchored in Human Psychology and Everyday Prevalence
Path dependence is deeply anchored in human psychology and manifests in various aspects of our lives. Consider the following examples:
- Personal Life: Career Choices Many individuals find themselves locked into a particular career path due to early educational choices or initial job opportunities. Over time, they become increasingly specialized, making it challenging to pivot to a different field. This path dependence stems from the inertia of previous choices and can limit personal growth and fulfillment.
- Business Scenario: Technology Adoption Businesses often face decisions regarding the adoption of new technologies. Path dependence comes into play when companies stick with outdated systems or technologies simply because they have invested heavily in them in the past. This reluctance to change may hinder innovation and render them less competitive in the long run.
- Public Policy: Political Systems The design of political systems can also be subject to path dependence. For example, the electoral systems, voting methods, or constitutional frameworks established in the past may shape the current political landscape and limit the range of choices available for reform. In such cases, historical decisions have a lasting impact on the democratic processes and policies of a nation.
Mental Biases and Psychological Underpinnings
Several mental biases contribute to path dependence:
- Status Quo Bias: Humans exhibit a preference for maintaining the current state of affairs. This bias makes it difficult to deviate from established paths, as the familiar feels safer and more comfortable, even if it may not be optimal.
- Endowment Effect: People tend to ascribe greater value to things they already possess. This bias can lead to a reluctance to abandon or change existing systems, as the perceived loss outweighs the potential gains associated with alternative paths.
- Anchoring Bias: Individuals often rely heavily on initial information or experiences when making subsequent decisions. This bias can lock decision-makers into a specific trajectory, as the initial path becomes the reference point against which all alternatives are evaluated.
Avoiding the Trap of Path Dependence
To avoid succumbing to path dependence, consider the following strategies:
- Foster Open-mindedness: Cultivate a mindset that embraces change and recognizes the value of exploring new paths. Challenge the status quo and question assumptions to avoid being trapped by historical choices.
- Conduct Thorough Analysis: When making decisions, thoroughly evaluate the available options, considering both the short-term and long-term implications. Seek diverse perspectives, gather relevant data, and assess potential consequences to ensure a more informed decision-making process.
- Embrace Flexibility: Recognize that decisions are not permanent and that adjustments can be made along the way. Embrace a growth mindset that acknowledges the potential need to change course when new information or opportunities arise.
Conclusion
Path dependence emphasizes the significance of historical decisions in shaping our present and future choices. By understanding the psychological biases that contribute to path dependence and employing strategies that promote open-mindedness, thorough analysis, and flexibility, individuals and organizations can navigate decision-making processes more effectively. Awareness and active avoidance of the path dependence trap enable us to break free from the constraints of the past and forge new paths towards innovation, growth, and success.