Introduction
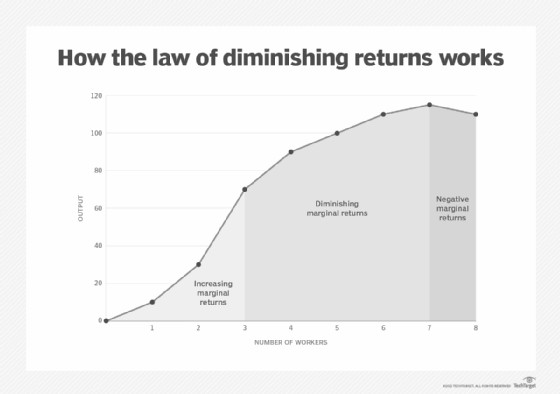
In the realm of decision-making, our pursuit of rewards and outcomes is often accompanied by a phenomenon known as the Law of Diminishing Reward. This mental model suggests that as we continue to invest time, effort, or resources into a particular endeavor, the incremental returns diminish over time. Understanding this concept is crucial in decision-making processes, as it allows us to evaluate the diminishing returns associated with our actions. Anchored in human psychology, the Law of Diminishing Reward is prevalent in our day-to-day lives and can help us avoid making irrational decisions contrary to our best interests.
The Relevance of the Law of Diminishing Reward in Decision-Making
The Law of Diminishing Reward highlights the need to critically assess the diminishing returns associated with our investments. By recognizing this principle, individuals and groups can avoid allocating excessive resources or efforts to areas where the returns have plateaued. This mental model is relevant in personal life decisions, business scenarios, and public policy-making, shedding light on the potential consequences of disregarding the diminishing rewards.
Occurrences of the Law of Diminishing Reward
- Personal Life Decisions: Consider a person’s pursuit of a hobby. Initially, engaging in the hobby brings a sense of joy and fulfillment. However, as time goes on, the novelty wears off, and the enjoyment derived from each subsequent session diminishes. Despite this diminishing reward, individuals may continue to invest significant time and resources into the hobby, neglecting other potentially more fulfilling pursuits.
- Business Scenarios: In the realm of business, the Law of Diminishing Reward is evident in marketing campaigns. Initially, a marketing campaign may yield substantial returns, attracting new customers and increasing sales. However, as the campaign continues, the impact on customer acquisition diminishes, reaching a point where the cost of sustaining the campaign outweighs the benefits. Ignoring this principle, businesses may persist with ineffective campaigns, resulting in wastage of resources and missed opportunities for more impactful strategies.
- Public Policy-Making: The Law of Diminishing Reward plays a role in public policy-making, particularly in the allocation of resources. Consider a government’s investment in infrastructure projects. Initially, the construction of roads, bridges, and public facilities can have a significant positive impact on economic development and quality of life. However, as the infrastructure becomes more extensive, the marginal benefits decrease, and the cost of maintaining and expanding the infrastructure rises. By neglecting the diminishing returns, policymakers may continue to invest in unnecessary infrastructure projects, diverting resources from other pressing needs such as education or healthcare.
Mental Biases and Psychological Underpinnings
Several cognitive biases contribute to falling prey to the Law of Diminishing Reward. The sunk cost fallacy is a prominent bias in this context, leading individuals to continue investing in a diminishing endeavor simply because they have already invested significant resources or effort. This bias prevents rational decision-making, as it fails to consider the diminishing returns and focuses on past investments instead.
Confirmation bias also plays a role by distorting perception and reinforcing the belief that continued investment will eventually lead to a breakthrough or improved returns. Individuals may seek information that confirms their expectations while neglecting contradictory evidence, perpetuating the cycle of diminishing rewards.
Identifying and Avoiding the Law of Diminishing Reward
To avoid succumbing to the Law of Diminishing Reward, it is crucial to cultivate awareness and employ strategies that foster objective decision-making:
- Regular Evaluation: Continuously assess the returns and benefits derived from an endeavor. Monitor the trajectory of rewards and be vigilant for signs of diminishing returns. Regular evaluation helps in identifying the point where further investment may not yield commensurate rewards.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine the optimal allocation of resources. Assess the trade-offs between investments and returns, considering the diminishing rewards associated with each option. This analysis enables more informed decision-making and guards against excessive investment in declining returns.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Embrace flexibility and adaptability in decision-making. Be open to changing strategies or reallocating resources when the returns begin to diminish significantly. Recognize that persisting with a diminishing endeavor may prevent exploration of new opportunities with higher potential returns.
- Diversification: Seek diversification in investments or pursuits to mitigate the impact of diminishing returns. By spreading resources across multiple endeavors, individuals and organizations can balance potential diminishing rewards with the possibility of discovering new sources of value and satisfaction.
Conclusion
The Law of Diminishing Reward reminds us of the diminishing returns associated with continued investment in an endeavor. By understanding and actively avoiding this mental trap, we can make more rational decisions that align with our best interests. Awareness of the Law of Diminishing Reward allows us to evaluate the diminishing returns and make adjustments to our strategies and resource allocations accordingly. By employing strategies such as regular evaluation, cost-benefit analysis, flexibility, and diversification, we can navigate decision-making with a keen eye on optimizing returns and avoiding the pitfalls of plateauing rewards.