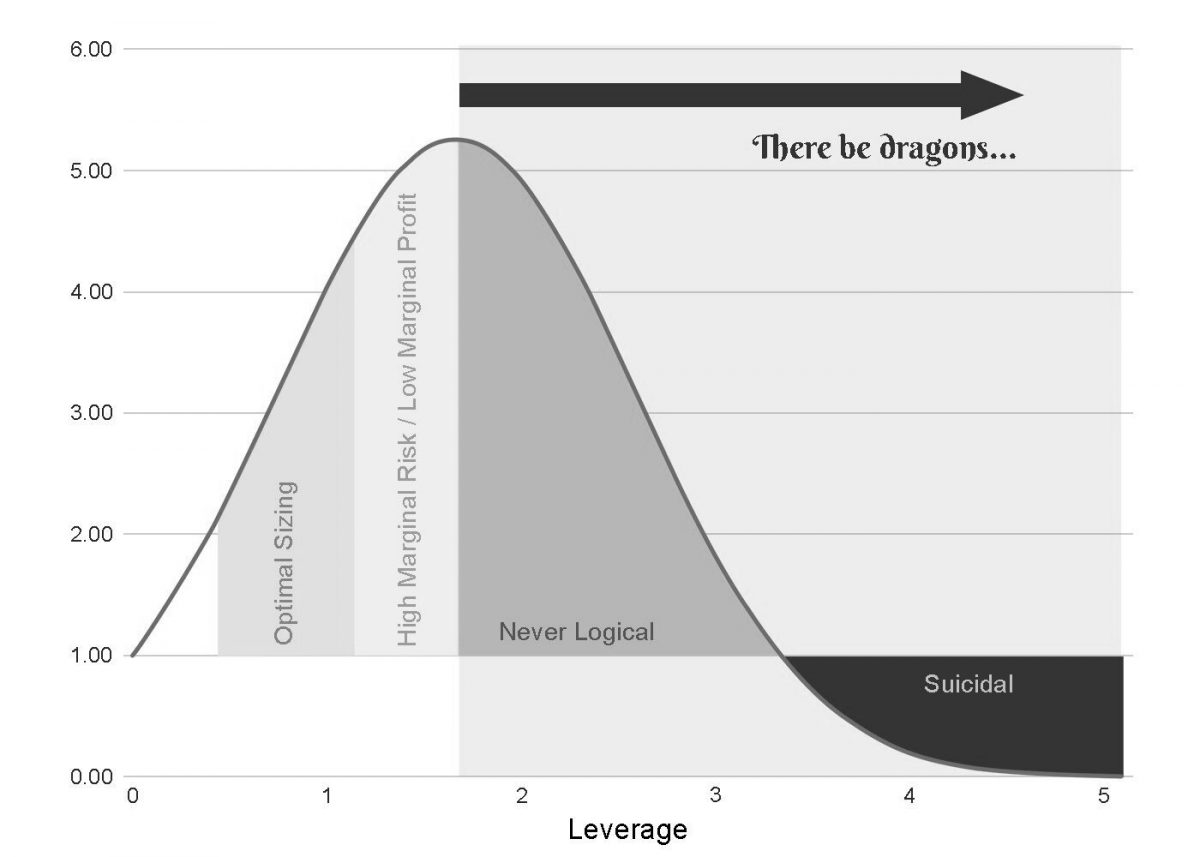
Introduction
In the realm of decision-making, understanding the mental models that shape our choices is invaluable. One such powerful model is the Kelly Criterion. This concept provides a systematic approach to managing risk and maximizing long-term growth. Anchored in human psychology, the Kelly Criterion influences our day-to-day lives, from personal decisions to business strategies and even public policy-making. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the Kelly Criterion as a mental model, its relevance in decision-making processes, and its prevalence in various contexts. We will examine real-life examples to demonstrate how individuals or groups, by disregarding the principles of the Kelly Criterion, make irrational decisions that undermine their best interests. Furthermore, we will explore the mental biases and psychological underpinnings that contribute to this bias, providing practical strategies to identify and avoid succumbing to the fallacies of the Kelly Criterion. By raising awareness and actively avoiding this mental trap, we can enhance our decision-making and achieve more favorable outcomes.
Defining the Kelly Criterion
The Kelly Criterion is a mathematical formula that provides a framework for determining the optimal allocation of resources in situations involving uncertainty and potential gains or losses. It guides decision-makers in estimating the size of their bets or investments based on the potential reward and the level of risk involved. The goal is to maximize long-term growth by striking a balance between capitalizing on opportunities and managing potential losses.
Relevance in Decision-Making Processes
The Kelly Criterion is relevant in decision-making processes where risk and reward are at stake. Whether it is managing personal finances, making investment decisions, or designing business strategies, understanding the optimal allocation of resources is crucial. By following the principles of the Kelly Criterion, decision-makers can avoid reckless behavior, achieve sustainable growth, and mitigate the adverse effects of poor judgment.
Prevalence of the Kelly Criterion in Our Lives
The Kelly Criterion is prevalent in various domains of our lives. Let’s examine three distinct examples to illustrate its occurrence
- Personal Life Decisions: Consider an individual planning to invest a significant portion of their savings in a new business venture. By applying the Kelly Criterion, they would carefully assess the potential returns and the associated risks. Instead of investing all their resources in a single venture, they would diversify their investments, allocating an amount proportional to the estimated growth potential and risk of each opportunity. By doing so, they minimize the risk of total loss and increase the chances of long-term success.
- Business Scenarios: In the business world, the Kelly Criterion guides decision-making when evaluating investment opportunities or allocating advertising budgets. For example, a marketing team assessing different advertising channels would analyze the potential returns and risks of each option. They would allocate resources to channels with higher expected returns and adjust their investments proportionally to achieve the optimal balance between growth and risk. Neglecting the principles of the Kelly Criterion might result in overspending on low-return channels or missing out on high-growth opportunities.
- Public Policy-Making: The Kelly Criterion can also inform public policy decisions involving resource allocation. For instance, when evaluating infrastructure projects, governments can apply the principles of the Kelly Criterion to estimate the potential returns and risks. By allocating resources proportional to the estimated growth potential and risk associated with each project, policymakers can optimize the use of public funds and maximize societal benefits.
Mental Biases and Psychological Underpinnings
Several mental biases contribute to disregarding the principles of the Kelly Criterion. One such bias is the Overconfidence Bias, where individuals tend to overestimate their abilities or the accuracy of their judgments. This bias can lead to excessively large bets or investments, disregarding the potential risks involved.
Additionally, the Herd Mentality can play a role in deviating from the principles of the Kelly Criterion. When individuals follow the crowd without conducting independent analyses, they may be swayed by popular opinion rather than considering the actual risk-reward dynamics.
Avoiding the Kelly Criterion Trap
To avoid succumbing to the fallacies of the Kelly Criterion, it is important to adopt a disciplined and objective decision-making approach. Here are some practical tips
- Conduct thorough research and analysis: Gather relevant data and perform comprehensive assessments to estimate potential returns and associated risks accurately. Avoid making decisions based solely on intuition or social pressure.
- Embrace diversification: Instead of concentrating resources in a single investment or opportunity, diversify your portfolio. This helps manage risk and increases the potential for long-term growth.
- Regularly review and update assessments: As circumstances change and new information becomes available, reassess your estimates of potential returns and risks. Be open to adjusting your resource allocation accordingly.
- Seek expert opinions: Consult with domain experts or professionals who possess specialized knowledge. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives and enhance your decision-making process.
Conclusion
The Kelly Criterion offers a systematic approach to decision-making, allowing individuals and organizations to optimize resource allocation and manage risk effectively. By understanding its principles and avoiding the associated biases, decision-makers can make more informed and rational choices. Embracing the principles of the Kelly Criterion empowers individuals and groups to navigate uncertainty, achieve sustainable growth, and avoid the pitfalls of irrational decision-making. Awareness and active avoidance of the fallacies of the Kelly Criterion enhance our ability to make objective judgments and ultimately lead to more favorable outcomes.