Introduction
In our fast-paced world, making decisions efficiently and effectively is crucial. However, the abundance of choices and information overload often hinder our decision-making process. This is where Hick’s Law, a mental model rooted in human psychology, comes into play. Understanding this concept is essential for streamlining decision-making and avoiding the pitfalls of analysis paralysis. In this blog post, we will explore Hick’s Law, its relevance in decision-making processes, its prevalence in our daily lives, and strategies to overcome its limitations.
Defining Hick’s Law and its Relevance in Decision-Making
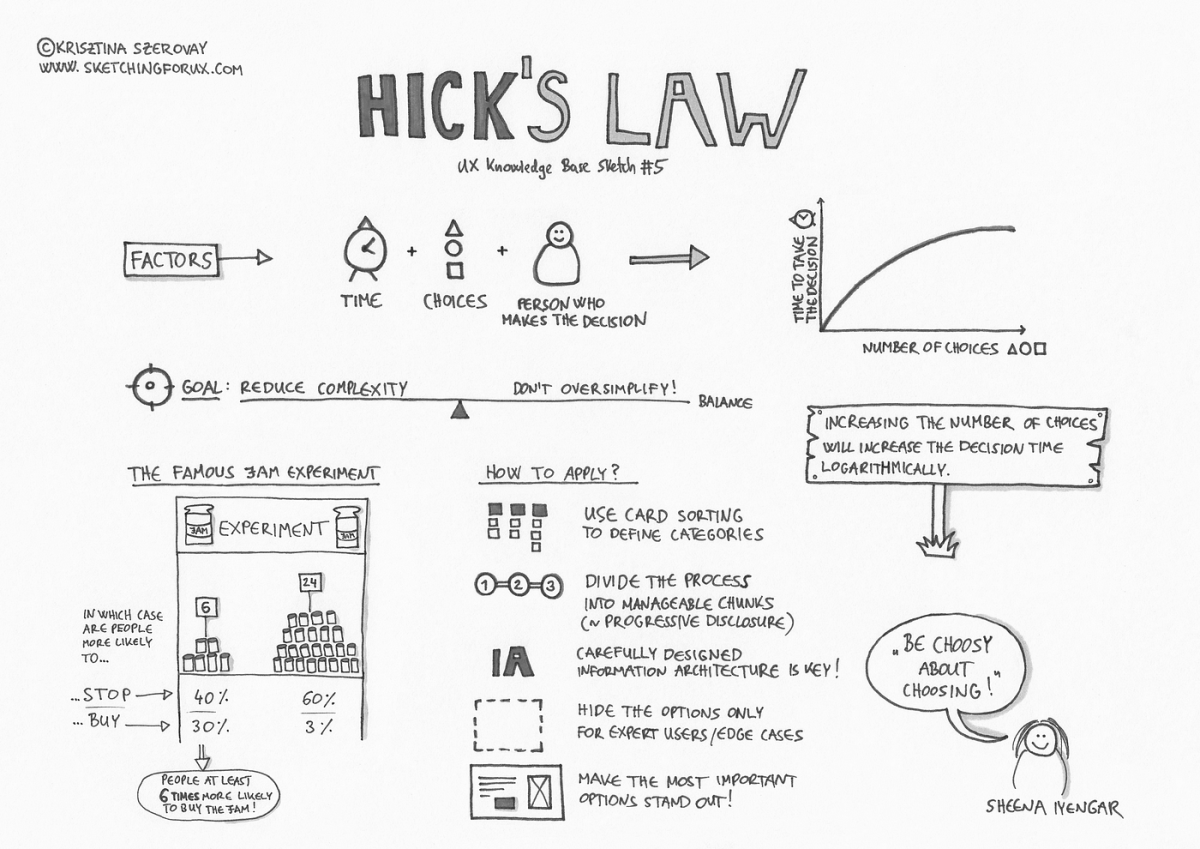
Hick’s Law states that the time it takes to make a decision increases with the number of alternatives or options available. In simpler terms, the more choices we have, the longer it takes for us to make a decision. This mental model is relevant in decision-making processes as it highlights the impact of decision complexity on our ability to reach a timely and effective conclusion.
Anchoring Hick’s Law in Human Psychology
Hick’s Law is anchored in human psychology and cognitive processes. One key psychological aspect is the limited capacity of our working memory. When faced with numerous options, our working memory becomes overwhelmed, leading to information overload and decision paralysis. Additionally, the fear of making the wrong choice, known as the fear of missing out (FOMO), can further contribute to the delay in decision-making.
Prevalence of Hick’s Law in Various Contexts
- Personal Life Decisions: Consider a person shopping for a new pair of shoes online. If they encounter a website with a vast array of options, ranging in color, style, and brand, they may spend an excessive amount of time scrolling, comparing, and contemplating their decision. The decision-making process becomes lengthy and frustrating, leading to decision fatigue and potential dissatisfaction with the final choice.
- Business Scenarios: In a business context, Hick’s Law manifests when organizations offer an extensive range of products or services. While providing variety can attract customers, it can also lead to decision paralysis. For example, a restaurant with an overwhelming menu can confuse customers and delay their decision-making process, potentially leading to frustration and a negative dining experience.
- Public Policy-Making: Hick’s Law also applies to public policy-making. When governments or policy-makers are faced with numerous options and considerations, decision-making can become protracted. This delay can result in missed opportunities, ineffective policies, or inadequate responses to societal issues.
Mental Biases and Psychological Underpinnings
Several mental biases contribute to Hick’s Law and its impact on decision-making. The paradox of choice bias, stemming from the fear of making the wrong decision, causes individuals to become indecisive when faced with an abundance of options. The status quo bias can also play a role, as individuals may default to familiar choices rather than explore new alternatives.
Additionally, decision fatigue, where the mental energy required for decision-making becomes depleted, can hinder effective decision-making. The sunk cost fallacy, where individuals consider their past investments and become reluctant to change their decision, further adds to the complexity and delay in reaching a conclusion.
Strategies to Identify and Avoid Hick’s Law
- Prioritize Decision Factors: Identify the key factors that matter most to you in the decision-making process. Focus on those factors and eliminate options that don’t align with your priorities. This approach streamlines the decision-making process and reduces the number of choices you need to consider.
- Utilize Decision Frameworks: Employ decision-making frameworks such as decision trees or weighted decision matrices. These tools help structure the decision-making process by systematically evaluating options based on predefined criteria. They provide clarity and facilitate a more efficient decision-making process.
- Set Time Limits: Allocate a specific time frame for decision-making. By setting time limits, you avoid excessive rumination and force yourself to make a decision within a reasonable timeframe. This approach helps prevent analysis paralysis and encourages more efficient decision-making.
- Seek External Perspectives: Consult with trusted individuals or seek external opinions to gain a fresh perspective on your decision. Sometimes, getting input from others can help simplify complex choices and provide clarity.
Conclusion
Hick’s Law reminds us of the challenges we face when making decisions in a world filled with options. Understanding this mental model allows us to navigate decision-making more effectively and avoid the pitfalls of analysis paralysis. By recognizing the psychological underpinnings and biases that contribute to Hick’s Law, we can employ strategies such as prioritizing decision factors, utilizing decision frameworks, setting time limits, and seeking external perspectives to streamline our decision-making processes.
Awareness of Hick’s Law and actively avoiding its negative effects empowers us to make timely, informed decisions that align with our goals and values. By simplifying the decision-making process, we can reduce decision fatigue, increase satisfaction with our choices, and ultimately achieve better outcomes in both personal and professional spheres.