Introduction
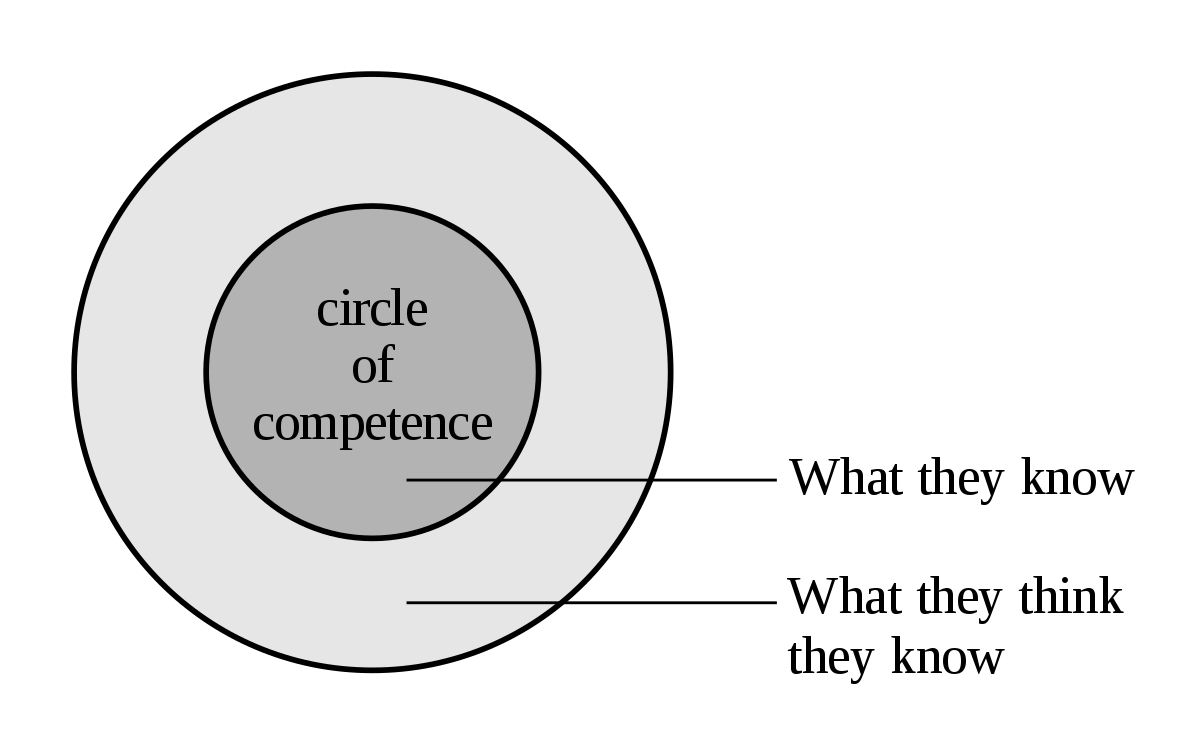
The Circle of Competence is a mental model that emphasizes the importance of understanding one’s knowledge and expertise boundaries in decision-making. Anchored in human psychology, this model highlights the significance of self-awareness and the ability to recognize and stay within one’s area of competence. By embracing the Circle of Competence, individuals can make more informed and rational decisions, avoiding the pitfalls of overconfidence and venturing into unfamiliar territories.
Defining the Circle of Competence and Its Relevance
The Circle of Competence refers to the range of skills, knowledge, and expertise in which an individual or group has a deep understanding and competency. It is the domain in which they can make reliable judgments and effective decisions. Recognizing and respecting the boundaries of one’s Circle of Competence is crucial for sound decision-making, as it prevents individuals from making uninformed or irrational choices based on limited knowledge or expertise.
The prevalence of the Circle of Competence in our day-to-day lives is evident in various contexts, including personal life decisions, business scenarios, and public policy-making. By staying within their areas of expertise, individuals can avoid making decisions that may have adverse consequences and instead focus on utilizing their strengths and knowledge effectively.
Examples of the Circle of Competence in Various Contexts
- Personal Life Decisions: Consider an individual making a significant investment decision. If they have expertise in real estate, it is within their Circle of Competence to evaluate real estate opportunities, assess market trends, and make informed investment decisions. However, if they venture into unfamiliar territory, such as stock market investments, without sufficient knowledge or expertise, they may make poor decisions that lead to financial losses.
- Business Scenarios: In the business world, the Circle of Competence plays a crucial role in strategic decision-making. A company specializing in software development, for instance, should focus on leveraging its expertise in that area. By recognizing their Circle of Competence, they can make informed decisions about product development, market positioning, and resource allocation. However, if they try to expand into unrelated industries without the necessary expertise, they may face challenges and make costly mistakes.
- Public Policy-Making: The Circle of Competence is also relevant in public policy-making. Policy experts, economists, and social scientists within a government body possess expertise in specific areas. By respecting their Circle of Competence, policymakers can rely on evidence-based decision-making and seek advice from relevant experts. If policymakers venture into domains outside their expertise, they risk making flawed decisions that can have detrimental effects on the economy and society.
Mental Biases and Psychological Underpinnings
Several mental biases contribute to the violation of the Circle of Competence. Overconfidence Bias can lead individuals to believe they have competence in areas beyond their expertise, resulting in flawed decision-making. Confirmation Bias can reinforce existing beliefs and prevent individuals from seeking alternative viewpoints or recognizing the limits of their knowledge. The Dunning-Kruger effect may cause individuals with limited competence to overestimate their abilities and venture into unfamiliar territories without adequate expertise.
Practical Strategies for Avoiding the Circle of Competence Trap
To avoid succumbing to the Circle of Competence trap, consider the following strategies:
- Self-Awareness and Reflection: Engage in introspection to assess your own areas of expertise and limitations. Reflect on past experiences to identify situations where you may have exceeded your competence boundaries.
- Seek Expertise and Diverse Perspectives: Acknowledge the value of expertise and seek advice and guidance from individuals with specialized knowledge in relevant domains. Embrace diverse perspectives to challenge your assumptions and broaden your understanding.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Cultivate a growth mindset and invest in ongoing learning and development. Expand your Circle of Competence by acquiring new knowledge and skills while recognizing the need for depth and specialization in certain areas.
- Collaborative Decision-Making: Foster a collaborative decision-making culture that encourages interdisciplinary collaboration and knowledge-sharing. By leveraging the collective expertise of a team, you can make more well-rounded and informed decisions.
Conclusion
The Circle of Competence is a powerful mental model that emphasizes the importance of understanding one’s expertise boundaries in decision-making. By recognizing and respecting these boundaries, individuals can avoid overstepping their competence and making irrational choices. The implications of the Circle of Competence extend to personal, business, and public policy contexts, highlighting the value of expertise and informed decision-making. By incorporating self-awareness, seeking expertise, embracing diverse perspectives, and nurturing a learning mindset, individuals can enhance their decision-making abilities and navigate complex challenges with greater success.
Throughout this post, we have referenced relevant academic studies, psychological research, and renowned works to support the concepts discussed. By exploring the Circle of Competence, we hope to equip readers with practical strategies and a deeper understanding of the importance of staying within one’s expertise boundaries for effective decision-making.