Introduction
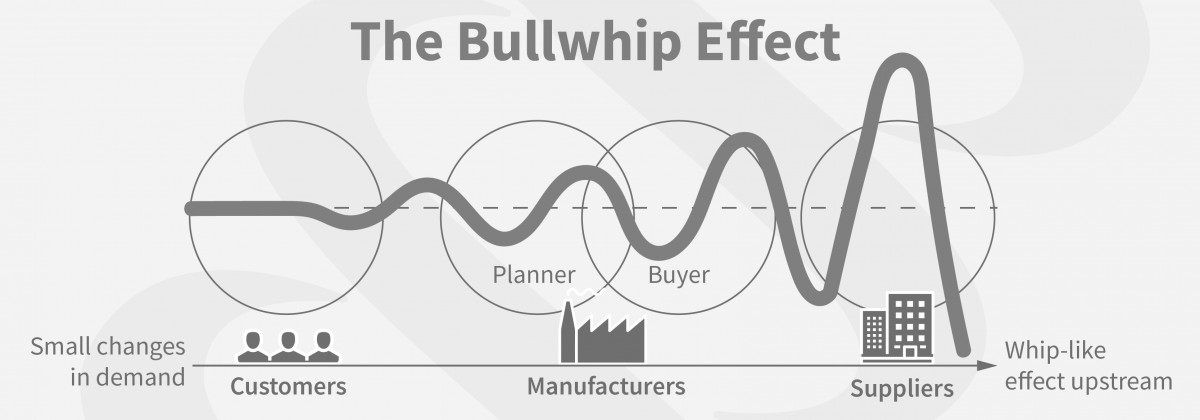
The Bullwhip Effect mental model describes the amplification of demand fluctuations along the supply chain, leading to exaggerated inventory fluctuations and inefficiencies. This phenomenon highlights the intricate relationship between decision-making processes and the cascading effects they can have on a broader system. Anchored in human psychology, the Bullwhip Effect is prevalent in our day-to-day lives and has significant implications for personal decisions, business operations, and public policy-making.
The Bullwhip Effect and Human Psychology
The Bullwhip Effect arises from several psychological tendencies that influence decision-making. One key aspect is our inherent aversion to uncertainty and desire to mitigate risk. As a result, individuals and groups tend to overreact to changes in demand or information, causing amplified fluctuations that ripple through the supply chain. This bias towards excessive caution or anticipation can lead to irrational decisions and unintended consequences.
Examples of the Bullwhip Effect
- Personal Life Decisions: Consider the scenario of panic buying during a natural disaster. In response to limited information and fear of scarcity, individuals often overestimate their needs and engage in excessive hoarding. This behavior creates artificial shortages and disrupts the supply of essential goods, causing inconvenience and further exacerbating the perceived scarcity.
- Business Scenarios: In supply chain management, the Bullwhip Effect manifests when each participant in the chain amplifies demand fluctuations. For instance, if a retailer receives an unexpected surge in demand, they may respond by increasing their orders from the distributor. The distributor, in turn, increases its orders from the manufacturer, and the manufacturer may overproduce to meet the inflated demand. This sequential amplification of demand fluctuations along the supply chain leads to inefficiencies, excessive inventory, and increased costs.
- Public Policy-Making: The Bullwhip Effect can also be observed in public policy-making. When policymakers respond to short-term changes or political pressures, they may enact legislation or policies with unintended consequences. For example, sudden changes in tax rates or regulations can create market volatility and disrupt business operations, leading to economic inefficiencies and uncertainty.
Mental Biases and Underpinnings
Several cognitive biases contribute to the occurrence of the Bullwhip Effect:
- Availability Bias: This bias leads decision-makers to give more weight to recent or easily accessible information. It causes them to focus on short-term fluctuations rather than considering the long-term stability of the system.
- Anchoring Bias: Decision-makers often anchor their decisions based on limited or distorted information. This bias can amplify demand fluctuations as decisions are made based on incomplete or inaccurate data.
- Herd Mentality: The tendency to follow the actions of others can exacerbate the Bullwhip Effect. If individuals or organizations observe others overreacting to changes, they may feel compelled to do the same, further amplifying demand fluctuations.
Identifying and Avoiding the Bullwhip Effect
To mitigate the Bullwhip Effect and make more objective decisions, individuals can employ the following strategies:
- Long-Term Perspective: Adopt a long-term perspective when assessing information and making decisions. Consider the broader system and the potential consequences of overreacting to short-term fluctuations.
- Information Sharing and Collaboration: Improve communication and collaboration among stakeholders in supply chains, business partnerships, or policy-making processes. Sharing accurate and timely information can help reduce uncertainty and minimize the amplification of demand fluctuations.
- Demand Forecasting and Data Analysis: Invest in robust demand forecasting models and data analysis to make informed decisions. By leveraging historical data and predictive analytics, decision-makers can better anticipate demand patterns and mitigate the effects of sudden fluctuations.
Conclusion
The Bullwhip Effect demonstrates the complex interplay between decision-making and the amplification of demand fluctuations along the supply chain. By understanding the psychological biases and cognitive tendencies that contribute to this phenomenon, individuals and organizations can make more rational decisions and avoid the pitfalls of overreacting to short-term changes. Awareness and active avoidance of the Bullwhip Effect can lead to more efficient supply chains, improved decision-making, and ultimately, better outcomes for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.