Introduction
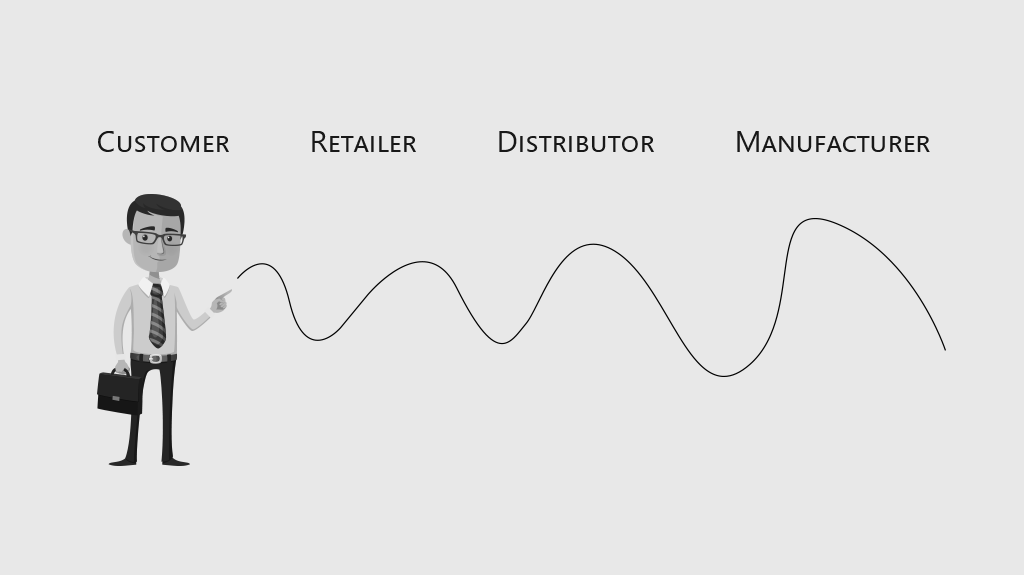
In the intricate realm of decision-making, the Bullwhip effect stands as a compelling mental model that sheds light on our tendency to make irrational choices, often contrary to our best interests. Stemming from a phenomenon observed in supply chain management, the Bullwhip effect describes how small fluctuations in consumer demand can amplify as they ripple upstream, resulting in excessive inventory fluctuations, distorted pricing, and inefficiencies. While originally rooted in business processes, this concept resonates far beyond the supply chain domain, finding relevance in various aspects of our daily lives. By understanding the psychological underpinnings and biases that contribute to this effect, we can enhance our decision-making abilities and avoid falling into its grip.
The Bullwhip Effect in Action: Examples from Different Contexts
- Personal Life Decisions: Imagine an individual who, caught up in the frenzy of a booming real estate market, decides to purchase a property without careful evaluation. This person’s decision is heavily influenced by the escalating prices and the fear of missing out on future gains. However, once the market corrects itself, the individual finds themselves trapped in a property that has lost its value, experiencing financial distress. In this scenario, the Bullwhip effect manifests as individuals exaggerating the demand and value of an asset based on exaggerated perceptions and limited information.
- Business Scenarios: Consider a retail company that notices a sudden surge in demand for a particular product category. Responding to this unexpected spike, the company hastily ramps up production, ordering excessive quantities from suppliers. However, the demand eventually tapers off, leaving the company with surplus inventory. This leads to losses, discounts, and increased holding costs. Here, the Bullwhip effect demonstrates how minor fluctuations in consumer demand can lead to significant amplifications, causing inefficient allocation of resources.
- Public Policy-Making: In the realm of public policy, the Bullwhip effect can be observed in decision-making processes driven by public opinion. Politicians, driven by the need to secure public support, may succumb to the influence of vocal interest groups, responding with exaggerated policy changes that cater to the loudest voices rather than the broader public interest. This often results in policies that oscillate between extremes, causing instability and inefficiency.
Psychological Biases and Underpinnings
Several mental biases contribute to the Bullwhip effect, amplifying its impact on decision-making. One such bias is the Availability Heuristic, where individuals overestimate the likelihood of an event based on the ease with which relevant examples come to mind. This bias leads people to assign greater importance to recent and vivid experiences, magnifying their influence on decision-making.
Another contributing factor is the Herd Mentality, driven by our innate desire for social conformity. When faced with uncertainty, we tend to follow the actions and opinions of others, even if they are based on flawed reasoning or incomplete information. This herd behavior exacerbates the Bullwhip effect by amplifying the fluctuations as they cascade through the network of decision-makers.
Moreover, our susceptibility to Confirmation Bias, the tendency to seek and interpret information that confirms our preexisting beliefs, plays a significant role in the Bullwhip effect. We selectively perceive and remember information that aligns with our opinions, reinforcing distorted beliefs and contributing to the amplification of demand fluctuations.
Recognizing and Mitigating the Bullwhip Effect
To avoid falling victim to the Bullwhip effect, it is crucial to develop self-awareness and cultivate a more objective decision-making process. Here are some strategies and tips to consider:
- Embrace Data-Driven Decision-Making: Relying on factual data and objective analysis can help mitigate the influence of biases. Seek diverse and reliable information sources, challenge your assumptions, and consider multiple perspectives before drawing conclusions.
- Foster Critical Thinking: Encourage a culture of questioning and skepticism. Challenge the prevailing narratives and assumptions, aiming to understand the underlying causes and potential biases in decision-making processes.
- Evaluate Long-Term Consequences: When making decisions, take into account the potential long-term effects rather than succumbing to short-term fluctuations. Consider the broader context, anticipate future changes, and analyze the potential impact of decisions beyond the immediate horizon.
- Diversify Information Sources: Expose yourself to a wide range of viewpoints and perspectives. Engage in conversations with individuals who hold different opinions, as this helps broaden your understanding and reduces the risk of echo chambers that reinforce distorted beliefs.
Conclusion
The Bullwhip effect serves as a powerful mental model that reveals the inherent biases and psychological mechanisms influencing our decision-making processes. By recognizing its prevalence in various aspects of our lives, we can proactively guard against the amplification of demand fluctuations, misperceptions, and suboptimal choices. Cultivating self-awareness, challenging our biases, and embracing more objective decision-making practices can help us navigate the complexities of decision-making with greater clarity and wisdom. By doing so, we empower ourselves to make informed decisions that align with our long-term goals and best interests.