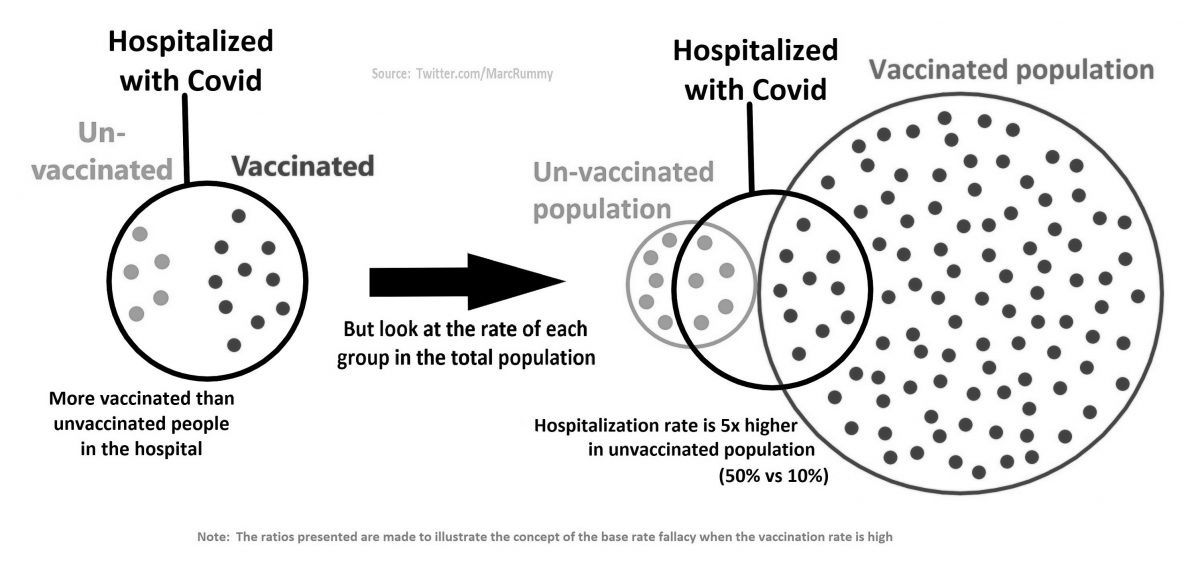
Introduction
The Base Rates mental model is a powerful tool that emphasizes the importance of incorporating relevant statistical information when making decisions. It recognizes that human psychology often overlooks base rates, the general prevalence of events in a population, in favor of anecdotal or vivid information. By understanding and considering base rates, we can make more rational and informed decisions that align with our best interests. This model is deeply rooted in human psychology and manifests in various aspects of our lives, from personal choices to business strategies and public policy-making. In this article, we will explore the concept of base rates, examine its impact on decision-making, explore associated biases, and provide practical strategies to avoid falling into the base rate fallacy.
The Role of Base Rates in Decision-Making
Base rates are crucial in decision-making as they provide a foundation for understanding the likelihood of different outcomes. They offer an objective perspective by incorporating statistical information about the general population. However, human psychology often defaults to personal experiences or vivid anecdotes, neglecting the importance of base rates. This can lead to irrational decision-making that disregards the actual probabilities associated with certain events.
Examples of Base Rates in Various Contexts
- Personal Life Decisions: Consider an individual making a career choice based on the success stories of a few acquaintances who achieved extraordinary success in a particular field. By focusing solely on these exceptional cases, the individual may disregard the base rate of success in that field, which might be much lower. This can lead to unrealistic expectations and misguided career decisions.
- Business Scenarios: In the business world, failing to account for base rates can have significant consequences. For instance, a startup may decide to invest heavily in a marketing campaign based on a single anecdote of a competitor’s remarkable success with a similar strategy. However, by neglecting the base rates of marketing campaign success in the industry, the startup may overlook the fact that most campaigns yield modest or even negative returns.
- Public Policy-Making: Base rates are also relevant in public policy-making. For example, when considering implementing a new security measure at airports in response to a recent incident, policymakers might overestimate the effectiveness of the measure based on the vividness of the incident. However, by neglecting the base rate of such incidents occurring, they might allocate resources inefficiently or implement policies that have minimal impact on overall safety.
Mental Biases and Underpinnings
Several cognitive biases contribute to the base rate fallacy. The Availability Heuristic is one such bias, where individuals rely on easily retrievable or vivid examples when estimating probabilities. This bias leads to an overemphasis on specific instances and a neglect of base rates.
Another bias relevant to base rates is the Representativeness Heuristic. This bias leads individuals to make judgments based on how closely an event or person matches a prototype or stereotype, without adequately considering base rate information. This can lead to flawed judgments and decision-making.
Confirmation Bias also plays a role in the base rate fallacy. People tend to seek and favor information that confirms their existing beliefs, ignoring evidence that contradicts their preconceived notions. This bias can prevent individuals from considering base rates objectively and adjusting their decision-making accordingly.
Identifying and Mitigating the Base Rate Fallacy
To avoid succumbing to the base rate fallacy, it is crucial to develop an awareness of our biases and implement strategies for more objective decision-making. Here are some practical tips:
- Gather and Assess Relevant Data: Actively seek out and analyze relevant base rate information before making decisions. Consider statistical data, research studies, and expert opinions to form a more accurate understanding of the probabilities involved.
- Challenge Personal Anecdotes: Be aware of the limitations of personal experiences and anecdotes. Remember that they may not accurately represent the base rates of a particular outcome.
- Use Bayesian Reasoning: Apply Bayesian reasoning, a statistical approach that combines prior probabilities (base rates) with new evidence to update beliefs. This method allows for a more nuanced and rational assessment of probabilities.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Engage in discussions with individuals who possess different viewpoints or expertise. This can help broaden your understanding of base rates and prevent tunnel vision.
Conclusion
Base Rates serve as crucial anchors for decision-making, enabling us to make more informed and rational choices. By acknowledging the prevalence of the base rate fallacy and understanding the associated biases, we can actively avoid this mental trap. Incorporating statistical information, challenging personal anecdotes, and utilizing Bayesian reasoning empower us to make decisions that align with reality and our best interests. Awareness of the base rate fallacy is essential for making objective decisions, whether in personal life, business, or public policy-making. Let us embrace the power of base rates and improve our decision-making capabilities.