Introduction
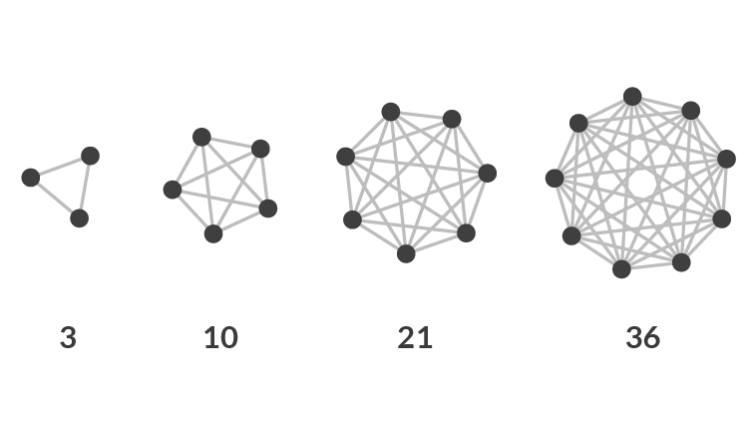
Metcalfe’s Law, formulated by Robert Metcalfe, states that the value of a network is proportional to the square of the number of its users. This mental model highlights the significance of network effects and their relevance in decision-making processes. Understanding Metcalfe’s Law allows individuals and organizations to recognize the potential benefits and pitfalls of network-based choices, anchored in human psychology and prevalent in our day-to-day lives. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the concept of Metcalfe’s Law, provide practical examples across personal, business, and public policy contexts, uncover associated biases, and offer strategies for informed decision-making.
The Relevance of Metcalfe’s Law
Metcalfe’s Law is highly relevant in decision-making processes as it sheds light on the exponential growth of value derived from networks. The model has become increasingly significant with the advent of digital platforms and the interconnectedness of our modern world. Recognizing the influence of network effects empowers individuals and organizations to make better choices by considering the potential impact on value creation, collaboration, and growth.
Anchored in Human Psychology and Everyday Prevalence
Metcalfe’s Law is anchored in human psychology and manifests in various contexts:
Personal Life: Social Connections
Consider the decision to join a social networking platform. The value of such platforms increases with the number of users. Falling prey to the Metcalfe Law fallacy might lead individuals to choose a platform solely based on its popularity rather than considering other factors such as privacy, functionality, or alignment with personal values.
Business Scenario: Platform Development
Companies often face choices when developing platforms or marketplaces. The success of these platforms depends on attracting a critical mass of users to create network effects. By underestimating the importance of building a vibrant user base, businesses may allocate inadequate resources, leading to a lack of engagement and ultimately failure.
Public Policy: Infrastructure Development
In the realm of public policy, the application of Metcalfe’s Law can be seen in decisions related to infrastructure development. For instance, the government may prioritize the expansion of broadband networks, understanding that the value of the infrastructure increases as more citizens gain access. Neglecting this principle could hinder economic growth and social connectivity.
Mental Biases and Psychological Underpinnings
Several mental biases contribute to the misconceptions surrounding Metcalfe’s Law:
Bandwagon Effect: People tend to follow the actions of others, assuming that popular choices are inherently valuable. This bias can lead individuals to join networks or platforms solely based on their size or popularity, without critically evaluating other aspects such as functionality or privacy concerns.
Confirmation Bias: Individuals may selectively seek information that supports their belief in the value of a network, overlooking potential drawbacks or alternative options. This bias reinforces the idea that a network’s value is solely determined by its size.
Availability Bias: People tend to overvalue readily available information and overlook less visible or emerging networks. This bias can hinder objective decision-making by favoring established networks over potentially more beneficial but lesser-known alternatives.
Avoiding the Trap of Metcalfe’s Law
To avoid falling prey to the fallacies associated with Metcalfe’s Law, consider the following strategies:
Critical Evaluation: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of network-based decisions beyond just the size or popularity of a network. Assess factors such as functionality, user experience, privacy, and alignment with personal or organizational goals.
Diverse Perspectives: Seek out diverse opinions and perspectives when evaluating network-based choices. Engaging with a variety of voices can provide a more balanced understanding of the potential benefits and drawbacks of different networks.
Long-Term Value: Consider the long-term value and sustainability of a network. Evaluate factors such as the network’s ability to adapt to evolving needs, its resilience to competition, and the potential for continued growth and innovation.
Conclusion
Metcalfe’s Law, with its emphasis on the value of network effects, has significant implications for decision-making in personal, business, and public policy contexts. By recognizing the psychological biases associated with this model and employing strategies for informed decision-making, individuals and organizations can navigate the networked world more effectively. Awareness, critical evaluation, and a focus on long-term value are essential in avoiding the trap of Metcalfe’s Law and making decisions that align with individual or organizational objectives.